Have you ever wondered what a domain is and how it influences your online presence?
Domains serve as virtual addresses, empowering websites and defining your online identity. Whether you're a seasoned user or just starting, understanding domains is essential in today's digital age.
In this blog, we'll demystify the concept of domains and reveal their untapped potential. Get ready to embark on an exciting journey that will reshape your understanding of the online world.
Let's dive in!
What is a Domain Name?
A domain name is like your digital address; it's how people find you on the internet.
Consider a domain name as the special name for your website. When people enter it in their browser, they're directed straight to your webpage. It's a personalized label that marks your space on the web, making sure that your site stands out in the vast ocean of the internet.
Here are some popular domain name examples you can look at: twitter.com, facebook.com, spotify.com, etc.
What are The Components of a Domain Name?
The components of a domain name can be divided into two parts. One is the name itself, and another is the domain name extension that stipulates the type of website it is using for.
Let me give you an example of the components of a domain name; look at the name ‘dorik.com.’ Here, ‘dorik’ is the domain, and ‘.com’ is the domain extension for this entire domain name.
What is The Difference Between a Domain Name and a URL?

(Image source: SproutRaise.com)
Now that you are well-versed with the components, let’s clarify a thing that many people get themself messed up with. Despite their visible dissimilarities, most people need help differentiating between domain names and URLs.
A URL, also known as Uniform Resource Locator, is a complete web address used to identify specific resources on the internet. An example of a URL is https://dorik.com/blog/how-to-create-a-real-estate-website, which has four different components.
The anatomy of this URL or the web address is-
A Protocol- the ‘https,’ also known as the hypertext transfer protocol secure.
A Domain name- dorik.com
A Subdirectory- ‘/blog/.’
A Path- the ‘/how-to-create-a-real-estate-website’ on the very last part of the URL.
There can also be a third-level domain (inside a domain name, e.g., 'www'), subdomains, and filenames inside a URL. The most important thing to notice is that a domain name is part of an URL. More precisely, a URL is a string of information beholding the entire address of a web page on the internet, where a domain name is part of a URL, a user-friendly form of an IP address.
Parts of a Domain Name

(Image source: CloudDNS)
A domain name can be mainly broken down into two parts. A ‘Second-Level Domain’ and a ‘Top-Level Domain.’
1. Second Level Domain (SLD)
A Second level domain name is a unique name that specifies your brand name from the other domain names. Second-level domain names are placed just left to the last dot of a domain name.
For instance, in dorik.com, the name ‘dorik’ is the second-level domain name placed just before the last dot of ‘.com.’
2. Top Level Domain (TLD)
The top-level domain (aka TLD) is the last part of a domain name, such as .gov, .com, or .org. TLDs are also known as ‘domain extensions’ in a Domain Name System. Regarding a domain name, TLD helps identify websites based on their purpose, content, and location.
For example, a domain name extension ‘.edu’ is usually used for educational institutions, while a ‘.gov’ extension or TLD is used for identifying US-based governmental institutions on the web.
Depending on their individual classification, let's explore some types of TLDs-
-
ccTLD: ccTLD or country-code Top Level Domains are two-lettered domain name extensions reserved for countries, dependent territories, or sovereign states. Organizations or institutions of a particular country or state can use their correspondent ccTLDs.
ccTLD helps to specify your location on the internet and allows search engines to crawl and showcase your website on Google search.
Some examples of ccTLDs are .in (India), .ca(Canada), .de (Germany), .io (British Indian Ocean Territory), .us (United States), etc.
-
gTLD: generic top-level domains are also known as gTLD, the most commonly and generally used TLD on the internet. Based on recent data of 2023, 1234 generic top-level domains are available on the internet.
Some examples of the generic top-level domain are .net, .com, .org, .ad, .co, .asda, etc. According to Statista, 52.5% of the global domains used the '.com' domain extension as of June 2022.
-
sTLD: Sponsored Top Level Domains (sTLD) are reserved and sponsored by private organizations or agencies that serve common services or themes. For example, the TLDs that indicate the likelihood organizations, like- businesses or governmental agencies, can be considered sTLDs. Searching for what are the domain names extensions for sTLD? You may look at some examples like- .museum, .mil, .edu, .marketing, .restaurants, .jobs, etc., for a clear understanding.
Sponsored top-level domains are considered as trustworthy. Websites with sTLDs help internet users find official information or data within no time.
How Does a Domain Name Work?
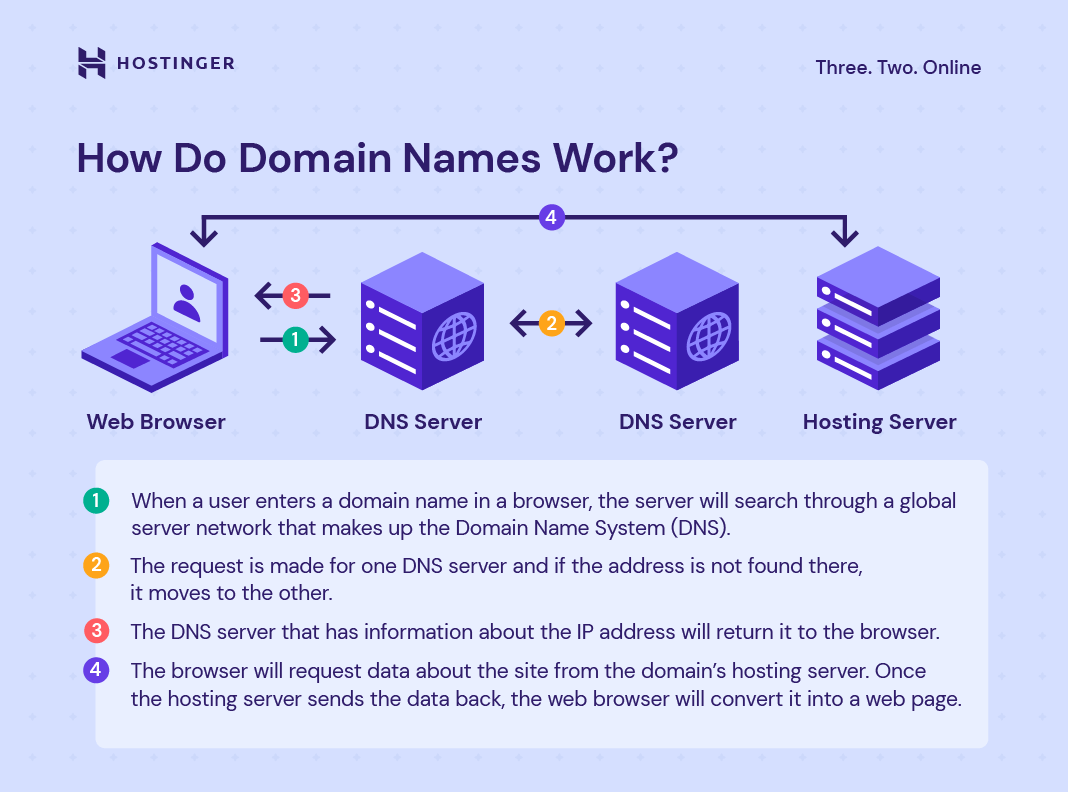
(Image source- Hostinger)
It is essential to understand how domain names work to know ‘what is a domain name’ in a more clarified view.
When a user searches for a domain name in their web browser, firstly, it sends a request to a global server from the Domain Name System (DNS).
If the address is not found on one DNS server, it sends the request to other servers.
When the request can find the information about that domain name’s IP address, the server will return that information to the user's browser.
Once the browser receives the DNS's associated IP address, it sends request information about the site to the domain’s hosting server. When the web hosting server sends back the information the user asks for, the web browser will convert the data into web pages and display it to the user.
Why Should You Buy a Domain Name?
Buying a domain name is a kind of investment. It has more benefits than deficiencies. Whether you are a service business owner looking for service website examples and planning to get online to make your sales process smoother. You need a domain name before creating a website for all these tasks.
For example, If you are making an artist website to sell artwork online, buying domain names will always serve you and assist you in staying up-to-date with your artwork’s online presence.
Benefits of Owning a Domain Name for Your Own
As domain names are the entry gate for creating a website, there are many extra credits for owning a domain name for yourself. As follows are some benefits of domain names:
-
Builds Brand Recognition.
-
Develop Credibility.
-
Increases Online Visibility.
-
Establish Authority.
With Dorik, it is easier and simpler for every user to set their own custom domain names and create their brand identity with the best no-code web builder. You can also learn how to configure a custom domain with your Dorik website.
Ready To Register a Domain Name and Get Online?
For every person who is looking to create a website, it is crucial to understand ‘What is a domain name’ and all the basic questions about this concept. While you are choosing the domain name for your website, consider the website’s content, keep the name simple, easy to spell, and memorable, and lastly, don’t forget to pick the perfect domain extensions.
For domain registration, check the availability of your desired domain name with a domain names generator, and go for the suggestion you prefer. Once you get the available name you are looking for, register it with a domain name registrar like- NameCheap, GoDaddy, and Google Domains.
Now, use your registered domain name to build your website and go live with your online presence in no time!





