Schema markup is structured data code that tells search engines exactly what your content means. It enables Google to display improved search results with additional details like ratings, prices, and key information, potentially increasing click-through rates.
Schema markup is structured data code that uses Schema.org vocabulary to help search engines understand your website content.
This guide covers why schema markup improves SEO performance, how structured data functions technically, and which schema types provide the highest impact for different website categories.
TL;DR:
-
Schema markup is structured data code using Schema.org vocabulary that helps search engines understand your content and display enhanced search results with ratings, prices, and key details
-
Rich snippets from schema markup can increase click-through rates by 20-30% compared to standard blue links, making your content stand out in search results
-
Focus on 8-10 core schema types like Organization, Product, Article, and LocalBusiness first, as these provide the highest SEO impact for most websites
-
JSON-LD format is Google's recommended implementation method - it's easier to maintain than microdata and doesn't slow down your website
Let’s Start at the Beginning - What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is standardized code that uses Schema.org vocabulary to clearly define and categorize website content, helping search engines understand what each page element represents. Search engines process HTML code and text content, but cannot differentiate between content types without explicit markup.
For example, "30 minutes" appears as generic text rather than being recognized as cooking time, and an ingredient list looks like any other bulleted content instead of recipe components.
Schema markup consists of HTML microdata, JSON-LD scripts, or RDFa attributes that explicitly label content elements using Schema.org vocabulary. It eliminates guesswork by explicitly labeling content types.
You specify: recipe, product, review, along with relevant attributes like ingredients, prices, or ratings.
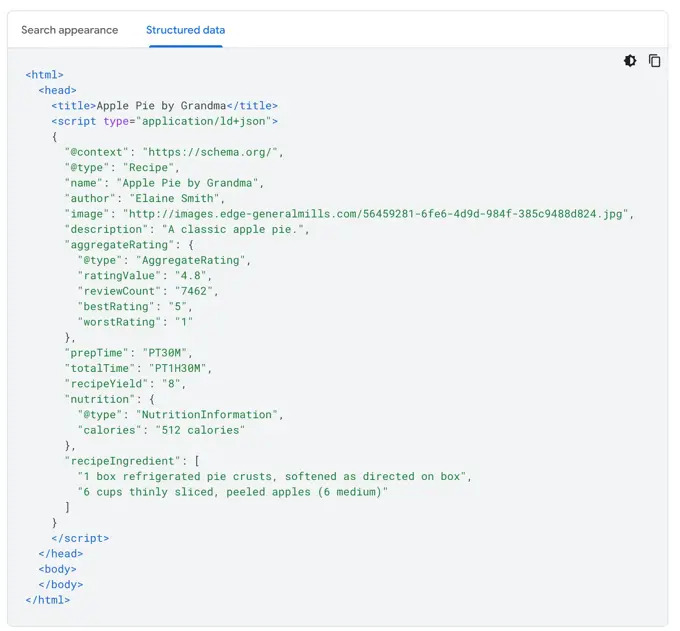
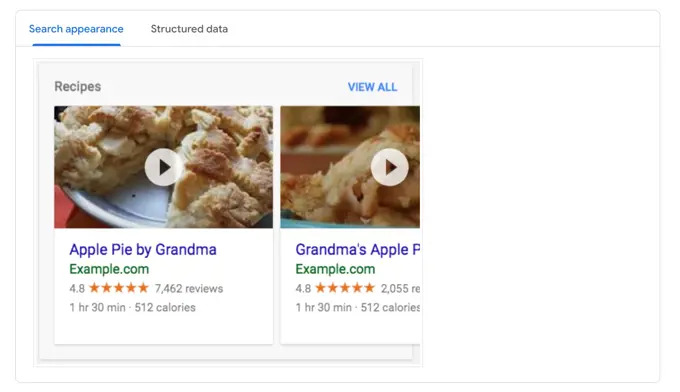
Source: Umbraco
Look at the images above to see how this works. The first image shows the actual code for an apple pie recipe - see how it clearly labels everything from "Recipe" to cooking time and ingredients.
The second image shows what happens next: Google shows this as a rich result with star ratings, cooking time, and calories right in the search results.
Without schema markup, search engines struggle to identify what your content represents and may display it as basic text links. With proper markup, they can accurately interpret your content and present it with enhanced formatting that attracts more user attention and provides immediate value to searchers.
Why is Schema Markup Important for SEO
Schema markup enables rich snippets, which can increase click-through rates by 20-30% according to multiple SEO studies. These enhanced search results display additional information like star ratings, prices, and availability directly in search listings.

Schema markup provides three primary SEO advantages:
-
Improved search visibility: Rich snippets make your content stand out in search results. Instead of plain blue links, you get eye-catching results with ratings, prices, or cooking times.
-
Higher click-through rates: Rich snippets with star ratings and additional details increase click-through rates by 17% compared to standard search listings (41% for non-rich results; 58% for rich results). A recipe with 5-star ratings and "Ready in 30 minutes" will get more clicks than a basic link.
-
Better user experience: People can quickly see if your content matches what they need. They don't have to guess or click multiple links to find basic information.
Think about it this way - without schema markup, your page shows up as just another blue link in a sea of search results. But if your competitors are using schema markup and getting rich snippets with star ratings and extra details, their results will grab attention while yours get ignored.
Schema markup does not directly improve search rankings, but higher click-through rates from rich snippets can indirectly signal content quality to Google, potentially supporting ranking improvements over time.
Also, schema plays a huge role in AI-powered search discovery. That’s why SEOs are turning to answer engine optimization as the future framework.
Finally, schema is one piece of the puzzle. Pair it with SEO best practices to get the most impact.
How Does Schema Markup Work?
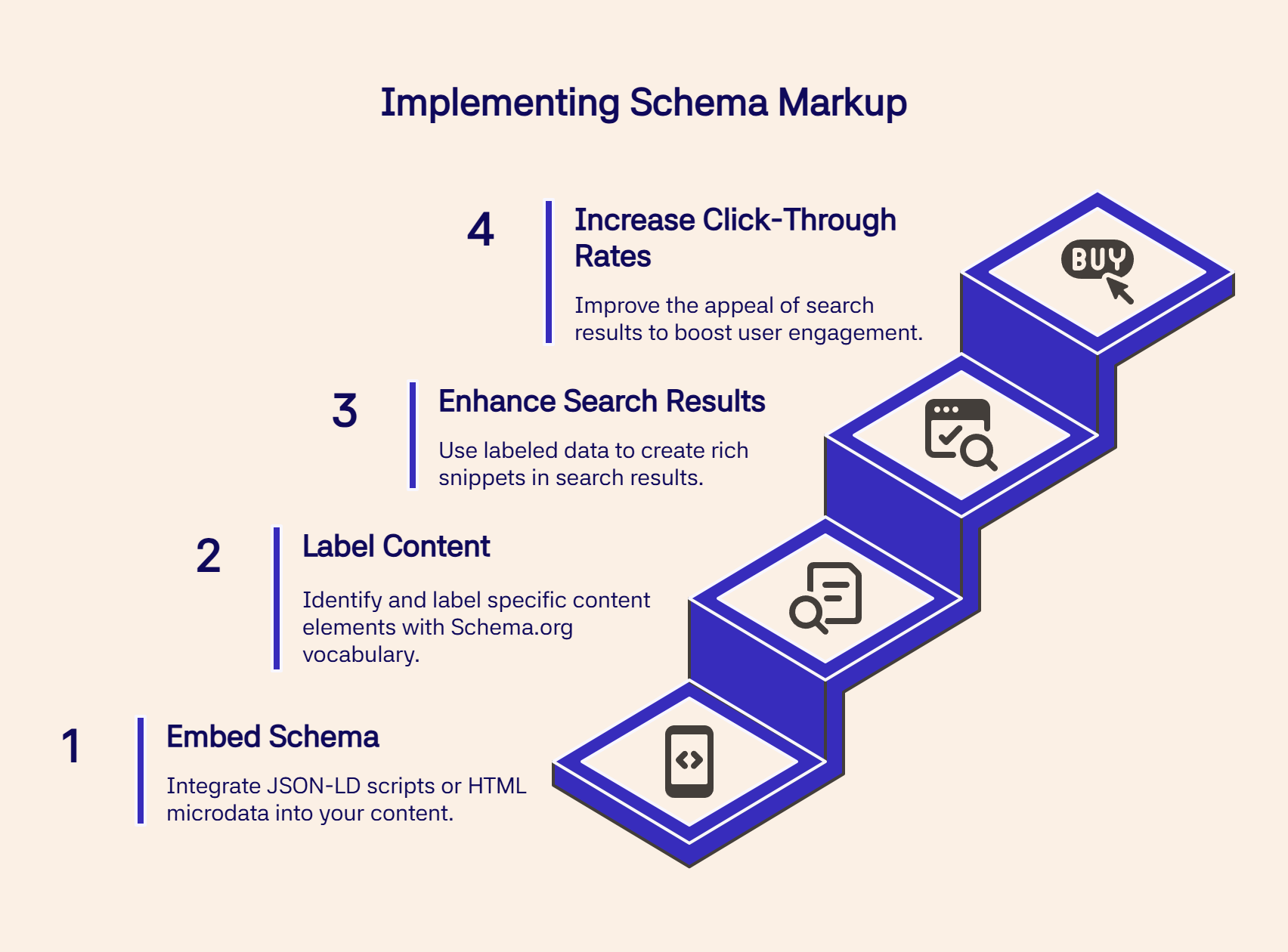
Schema markup uses Schema.org vocabulary to identify information types for search engines. Implementing it follows a 4-step process that transforms regular content into rich search results:
-
Embed Schema Markup: You embed JSON-LD scripts or HTML microdata using Schema.org vocabulary to label content elements like @type, name, description, and specific properties for each content type. This creates structured data that search engines can parse and process efficiently.
-
Label Content Elements: Instead of search engines guessing what your content is about, you're giving them direct hints. You can label specific text as a product name, review rating, event date, or price.
-
Search Engine Processing: Search engines use this labeled information to create enhanced search results with extra details like star ratings, prices, or event dates.
-
Enhanced Search Results: Schema markup does not directly improve search rankings. Rich snippets make search results more appealing, increasing click-through rates.
Here's an example: A product page displays 'Price: $29.99' as regular text. With schema markup, you wrap this in structured data: '"price": "29.99", "price, currency": "USD", which explicitly identifies the price value and currency for search engines.
Now search engines know exactly what it is and can display that price directly in search results. It's like adding clear labels to everything on your webpage so search engines don't have to guess what anything means.
Tip: Implementing schema is smoother on SEO-focused builders. Here’s a list of the best website builders for SEO to help you choose the right foundation.
Types of Schema Markup
Google supports over 30 schema markup types, but 8-10 core types handle most website needs. Focus on Organization, Product, Article, and LocalBusiness schemas first, as these provide the highest impact for most websites.
Let's explore some of the most commonly used types that can make the biggest impact on your search results.
Organization
Organization schema markup enables Google Knowledge Panels that display your business name, logo, founding date, headquarters address, social media profiles, and description directly in search results. This markup is essential for brand recognition and credibility.
This markup enables Google Knowledge Panels that prominently display your business information alongside search results, particularly for brand name searches.
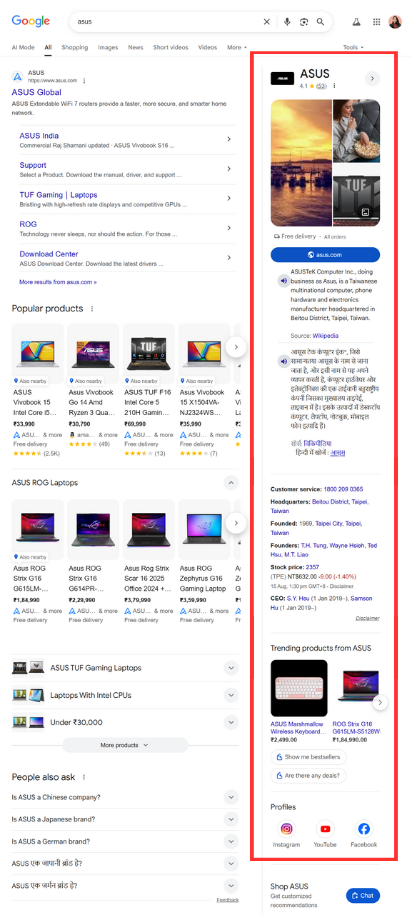
As you can see in the image above, ASUS's knowledge panel shows their logo, description, founding details, headquarters location, and even links to their social media profiles - all because they've implemented organization schema markup properly.
Product
Product schema markup displays price, currency, stock availability, star ratings, review count, shipping options, and promotional pricing directly in search results. This markup is essential for e-commerce competitiveness, as products without rich snippets appear less trustworthy to shoppers.
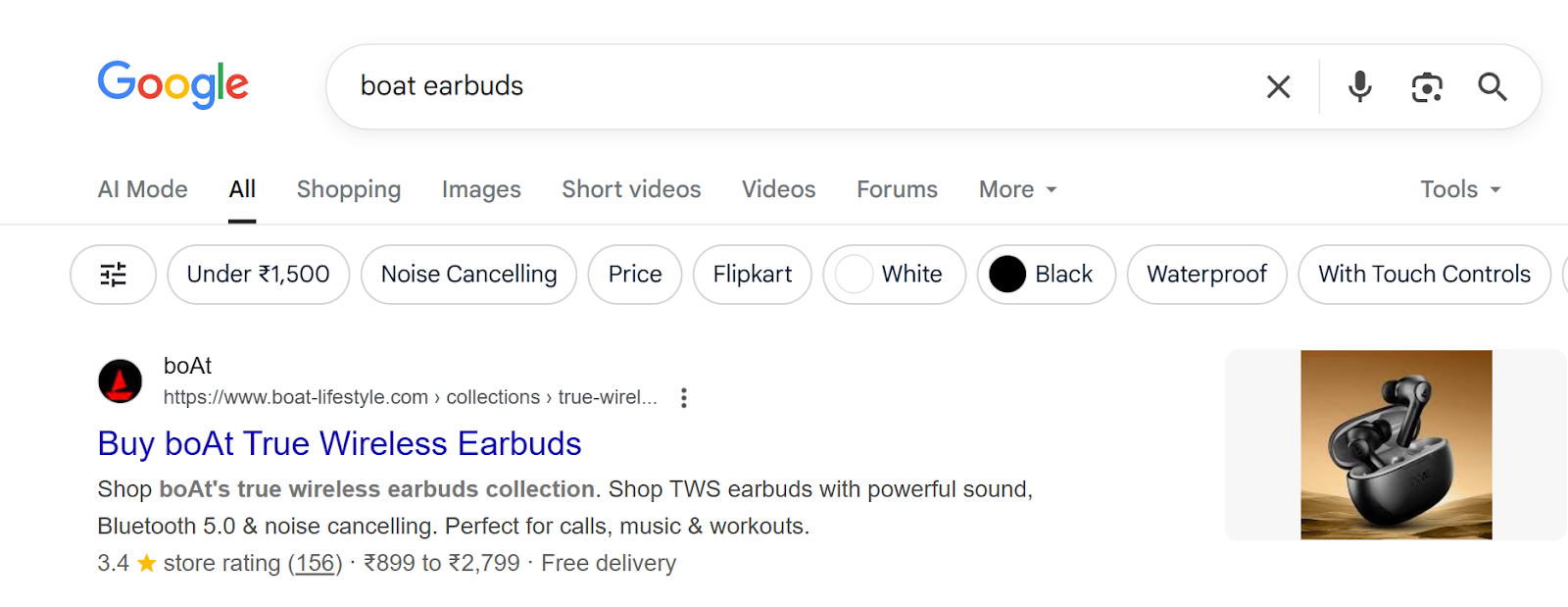
The image shows product markup displaying: 3.4-star rating, 156 reviews, price range ₹899-₹2,799, free delivery, and product image. Users can quickly assess if this product meets their needs without clicking through.
This markup is essential for e-commerce stores since it makes your products more competitive in search results and helps shoppers make faster purchasing decisions by providing all the key details upfront.
Article Markup
Article markup helps search engines understand news articles, blog posts, and sports articles, making your content eligible for rich snippets in Google Search and Google News.
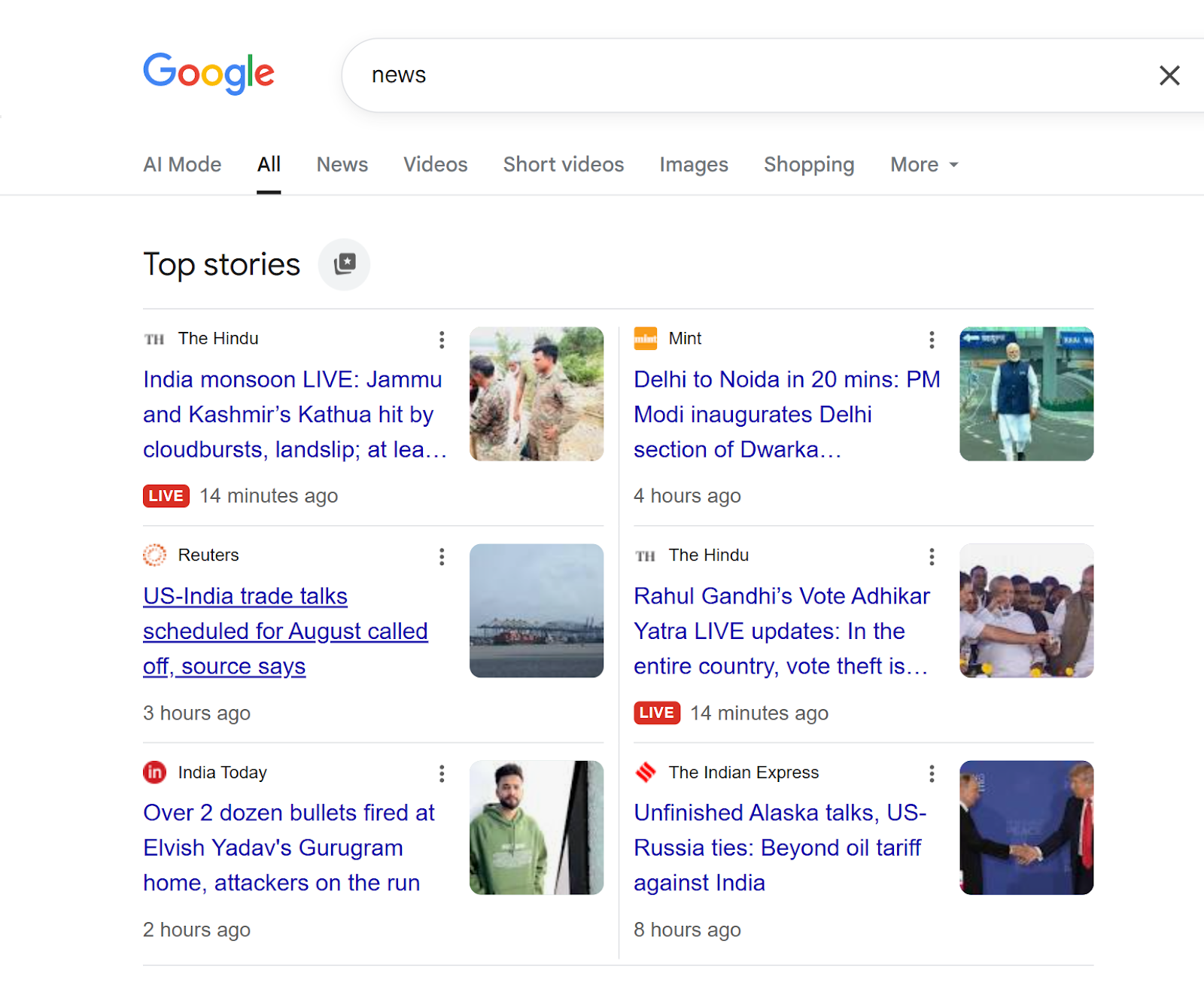
As shown in the image above, this markup allows your articles to appear in Google's "Top stories" section with proper formatting - displaying the publication source, headlines, timestamps, and even "LIVE" indicators for breaking news.
Carousel
Carousel schema markup groups related content from your website into horizontal scrolling search results. This format typically appears for event listings, product collections, restaurant locations, or article series when Google identifies multiple relevant items.
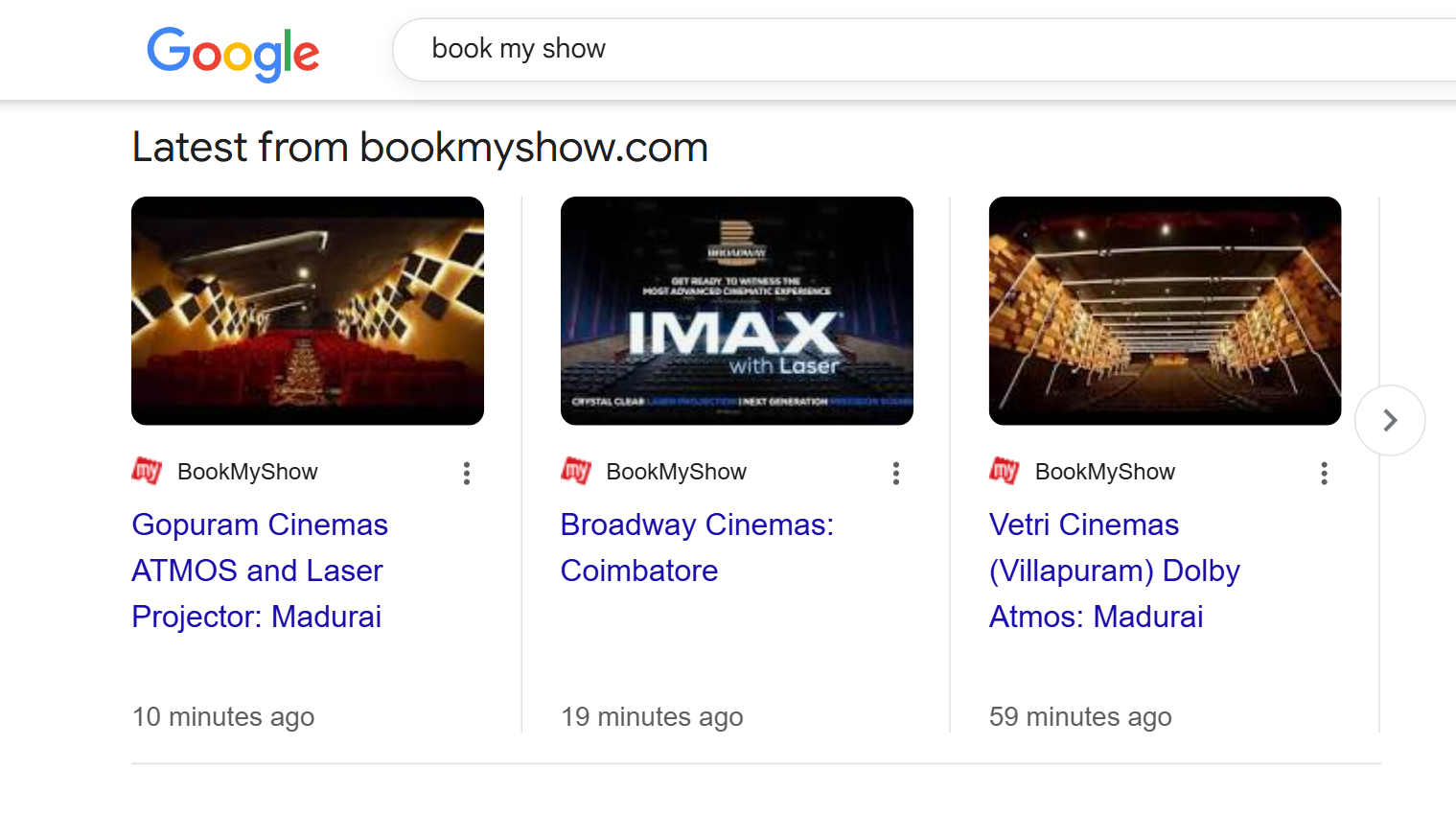
In the image above, you can see how BookMyShow's search results appear as a carousel showing different cinema locations - Gopuram Cinemas, Broadway Cinemas, and Vetri Cinemas - all displayed side by side with images, timestamps, and venue details.
This carousel format makes it easy for users to browse multiple options without having to scroll through separate search results.
Merchant Listing
Merchant listing markup is designed specifically for product pages where users can actually make a purchase. This schema helps display key buying information right in the search results.
It can show important purchase details like pricing and discounts (regular prices, sale prices, and current promotions), stock availability (whether items are in stock, on back order, or sold out), and shipping information (delivery estimates, shipping fees, and return policies).
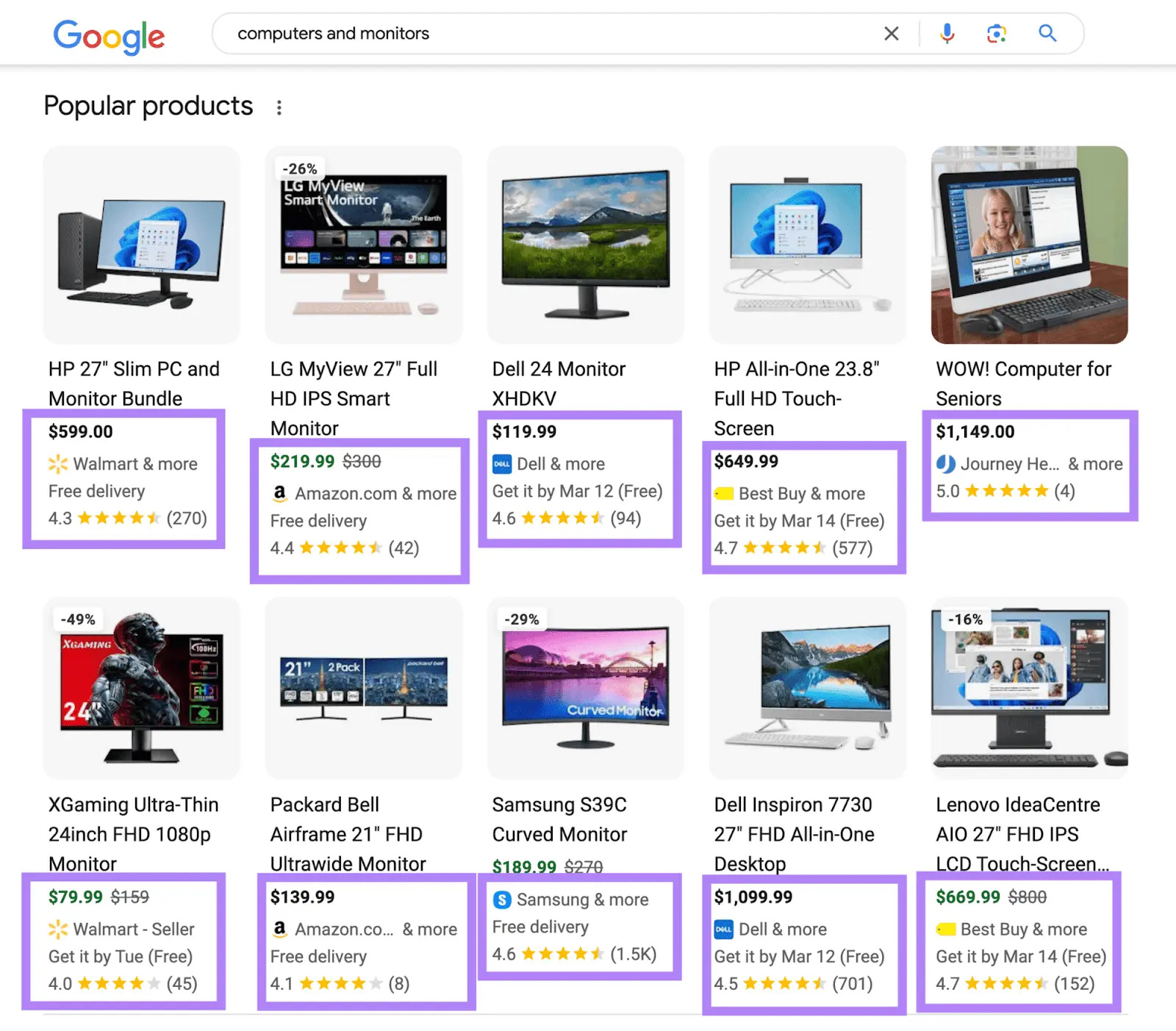
Source: Semrush
As you can see in the image above, Google's "Popular products" section shows exactly this type of information - prices, star ratings, retailer names like "Walmart & more" or "Amazon.com & more," delivery options like "Free delivery" and "Get it by Mar 12," and even discount percentages like "-26%" or "-49%."
This markup is perfect for e-commerce websites and online retailers who want to give potential buyers all the essential purchase information directly in search results, making it easier for shoppers to compare options without clicking through multiple pages.
Image Metadata
Image metadata schema markup helps search engines understand details about your images beyond just what they show. When you add image metadata markup, Google Images can display additional information about your images, including photographer credits, usage rights, and licensing details.

Source: developers.google.com
This markup is especially useful for photographers, e-commerce sites, and content creators who want to protect their work or provide licensing information.
Google can display information like license details, creator credits, and usage rights directly in Google Images, including features like the "Licensable" badge.
You can include details like the author, content location, date published, description, and even technical camera settings (EXIF data) like exposure time and aperture settings.
This helps your images stand out in search results and provides valuable context to users looking for specific types of visual content.
Logo
Logo schema markup tells Google which image to use as your brand's official logo in search results. This prevents Google from randomly picking any image from your website to represent your company in the Knowledge Graph or search listings.

As you can see in the Dorik search results above, Google displays consistent, recognizable logo variations across different sources - the wordmark logo, the blue icon version, and branded content. This organized presentation happens because Dorik has implemented logo schema markup properly.
Without this markup, your brand search might show random screenshots, product images, or unrelated visuals instead of your actual logo. The markup ensures your brand appears professional and consistent whenever people search for your company name.
Recipe
Recipe schema markup creates enhanced search results showing 5-star ratings, total review count, prep time, cook time, calorie count, and recipe images. This markup also enables recipe carousels in Google Images and recipe voice search compatibility.
Source: developers.google.com
The mockup above shows recipe markup in action - each result displays star ratings (4.7, 4.6, etc.), review counts, cooking times, and food images. This visual format makes recipes more clickable and helps users quickly identify what they want.
Recipe markup includes ingredients, prep time, cooking time, nutrition info, and instructions. It's essential for food bloggers since it also enables recipe badges in Google Images and recipe carousels.
Sitelinks Search Box
Sitelinks search box markup adds a search function directly within your brand's search results, letting users search your website without visiting it first. This creates a more interactive and useful search experience for people looking for your brand.
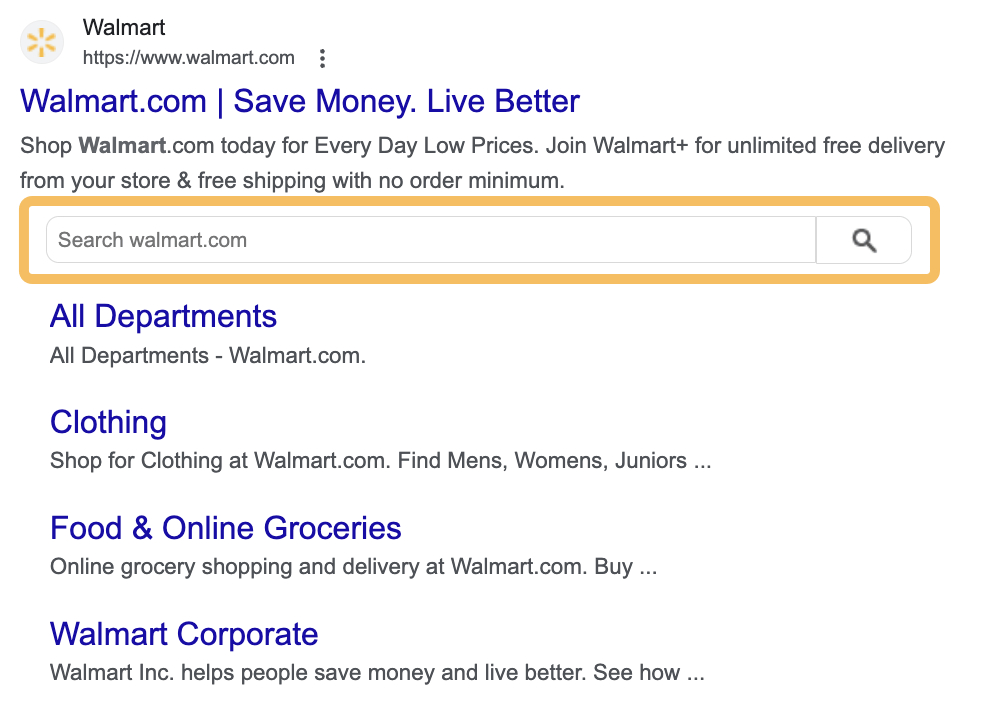
Source: Ahrefs
In the Walmart example above, you can see this in action - there's a search box right in the search result that says "Search walmart.com" along with sitelinks to important pages like "All Departments," "Clothing," "Food & Online Groceries," and "Walmart Corporate."
Users can either search directly or click these quick links.
This markup is particularly valuable for large websites with lots of content, as it helps users find specific products or pages faster and keeps them engaged with your brand right from the search results page.
FAQs
What’s the difference between structured data and schema markup?
Structured data is any organized data that helps search engines understand content. Schema markup is a specific type of structured data that uses Schema.org vocabulary to label content elements like products, reviews, or recipes. All schema markup is structured data, but not all structured data is schema markup.
What’s the difference between JSON-LD and Microdata for schema markup?
JSON-LD is a script-based format that adds schema markup in a separate block of code, making it easier to implement and maintain. Microdata is embedded directly within the HTML tags of a page, which can make the code harder to manage. Google recommends JSON-LD for schema markup.
Can schema markup improve my Google ranking?
Schema markup does not directly improve rankings, but it increases click-through rates by enabling rich snippets. Higher engagement signals can indirectly support ranking improvements by showing Google that users find the content valuable.
Will schema markup slow down my website?
Schema markup will not slow down your website. JSON-LD scripts are lightweight and load quickly, while Microdata is embedded within existing HTML. Both formats add minimal code and have no measurable impact on site speed.
Can adding the wrong schema markup hurt my SEO?
Adding the wrong schema markup can confuse search engines and prevent rich snippets from appearing. While it usually does not cause direct penalties, misleading or spammy markup can violate Google guidelines and result in manual actions that hurt SEO visibility.
Which pages on my site should have schema markup?
Pages that provide key information for users should have schema markup. These include homepage (Organization), product pages (Product), articles or blogs (Article), recipes (Recipe), local business pages (LocalBusiness), and FAQ or event pages. Focus on markup that highlights the most valuable content.
How do I implement schema markup on my website?
Implement schema markup by adding JSON-LD scripts or Microdata into your page code. Use Schema.org vocabulary to label elements like name, price, or rating. Test your markup with Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema Validator to ensure proper implementation.
What’s the easiest way to add schema markup to my website?
The easiest way to add schema markup is by using JSON-LD, which requires placing a script tag in the HTML head or body. Non-technical users can use tools like Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper, WordPress plugins (e.g., Rank Math, Yoast), or website builders with built-in schema options.
Can I use multiple schema types on the same page?
Yes, you can use multiple schema types on the same page if they accurately describe the content. For example, a recipe page can use Recipe, Review, and VideoObject schema together. Just ensure the markup matches the visible content and follows Google’s structured data guidelines.
How do I test if my schema markup is working?
Test your schema markup using Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema.org’s Schema Markup Validator. These tools show which elements are detected, highlight errors, and preview how rich snippets may appear in search results. Always validate after implementation to confirm accuracy.
How long does it take for schema markup to show in search results?
Schema markup can take several days to a few weeks to appear in search results. Google must first crawl and index your page before showing rich snippets. Implementation does not guarantee display, as Google decides based on content quality and relevance.
Wrap Up
Adding schema markup turns basic search listings into enhanced results that showcase ratings, pricing, and important details directly in Google's search results. You don't need every type - just focus on what's relevant to your business, like Organization, Product, or Recipe markup.
While schema doesn't directly boost rankings, it makes your results more appealing and clickable. In today's competitive search landscape, that extra visibility can make all the difference.
Schema markup improves visibility, but to maximize results, it should work hand-in-hand with a site builder optimized for SEO. Explore why Dorik is best for SEO to see how platform-level features amplify structured data efforts.





